Introduction
The main focus of this document is not to provide extensive theory on testing, but rather to suggest a mentality for our testing activities and to provide some helpful guides.
Primary goals
What do we want to achieve with the time we invest into tests:
- Catch errors as fast as possible
- Catch problems in all different issue categories
- Create understanding and transparency, which code has passed which quality gate. In order to achieve this we must also
- Value good and maintainable test code
- Provide structures that reduce time and obstacles to add new tests
General principles for testing
Principles that we should follow in our test activities result resulting from the primary goals:
- Test as "small as possible" i.e. fail fast
- view test code as part of code base -> same quality concerning reusablility, robustness, readability etc.
- do not forget error cases when testing, they are at least as important
- must be automated
From the "test as small as possible" principle it follows that a feature should always be tested on the smallest possible level. If e.g. the code around is organized in a layered fashion the test should if possible only test one layer and the adjacent layer should be covered by separate tests. Other kinds of tests that test a user feature in a broader scope should only be used as additional security mechanism to ensure that the components work correctly together or to prove that a user feature works from end to end.
Types of errors
Since the goals are distributed in very different areas of the development process, there's not one magic kind of test that will detect all of the possible issues. A multi-stage strategy for error detection and handling must be defined to effectively handle the possible error scenarios.
This section lists the different types of possible error scenarios and lists which measures we use to reduce the risk of running into these problems. The types of tests mentioned in these measures are further explained in the next section.
Platform issues
Description: platforms behave differently; underlying library or driver was updated, now errors occur.
Measures:
- Build every patch before mainline
- Run all unit tests (including sandwich tests) on all targets nightly
- Run renderer tests on all targets nightly
Code Issues
Description: errors in implementation
Measures:
- Build/Run unit tests every patch before mainline
- static checking tools nightly for example coverity/teamscale (*todo)
- dynamic checking tools nightly for example valgrind/sanitizers
Complex Code Issues
Description: e.g. race conditions, dead-locks, use-after-free, memory leaks
Measures:
- static & dynamic checking tools nightly for example coverity/teamscale/valgrind/sanitizers
Runtime Issues
Description: all kinds of possible runtime behavior
Measures:
- real world stress tests
- top level smoke tests run nightly on all targets
Performance Issues
Description: Performance drops unnoticed / in certain cases
Measures:
- performance tests in critical areas (renderloop, scene loading, scene transfer, latency) (*todo)
Integration Issues
Description: wrong usage of RAMSES in other applications
Measures:
- Continuous delivery enables early customer integration and testing
- Provide example applications showing usage
- Customer documentation
Customer Feature Tests
Description: Customer feature exposes unexpected behavior, graphic artefacts, wrong content, ...
Measures:
- Top level smoke tests run nightly on all targets
Requirement/Specification Issues
Description: Requirements change during development, are understood wrong or are missing
Measures:
- Agile development allows change of requirements every sprint. Customer can review at early product stage.
Types of tests
Unit test
- per class
- google test based
ideally executed:
- per patch on build server for selected platforms
- nightly for all platforms
Sandwich test
- on component level or crossing multiple layers
- google test based
ideally executed:
- per patch on build server for selected platforms
- nightly for all platforms
Rendering test
- sandwich test that executes all steps from scene to rendering of a pixel
- custom test framework
ideally executed:
- with software renderer per patch on build server
- nightly for all platforms
Top level smoke test
- tests end-to-end executing a top-level Ramses feature
- test with binary deployment, real network communication
- custom python-based test framework
ideally executed:
- nightly for all platforms
Stress test
- sandwich or smoke test under extreme load
- python-based test framework
ideally executed:
- per patch on build server for selected platforms
- nightly for all platforms
Performance test
- tests performance-critical parts of Ramses
- TODO
ideally executed:
- per patch on build server for selected platforms
- nightly for all platforms
Guide: which kind of test(s) should be used for a patch
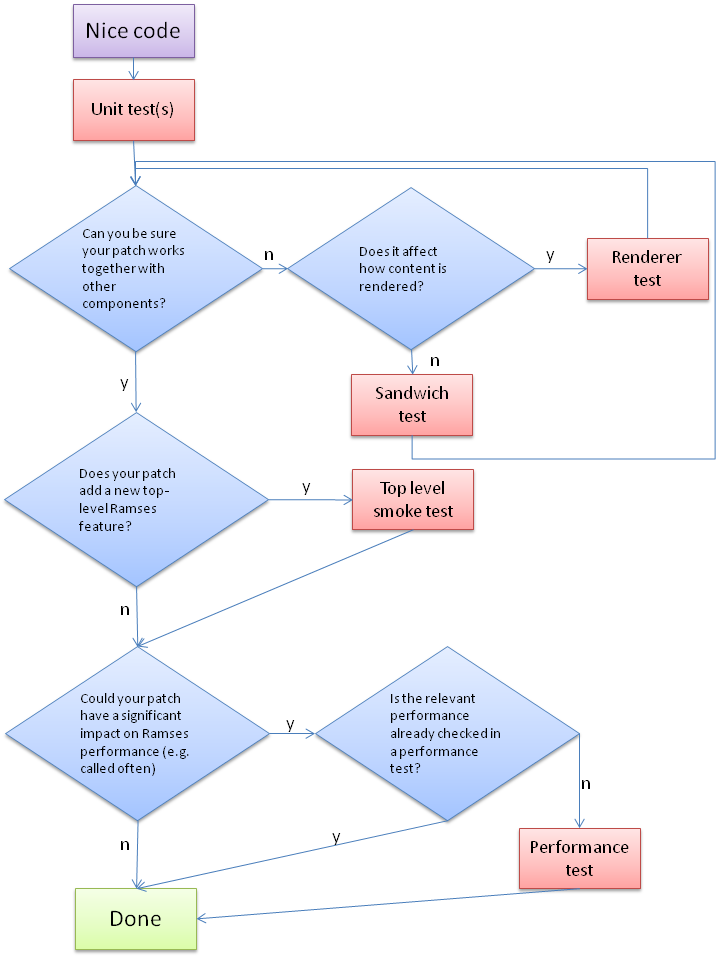
Guide: which kind of test(s) should be used for a patch


